Graph Coloring using Backtracking in C
In this, we have been given a graph G and "m" colors. We have to colour out graph in such a way that NO 2 ADJACENT NODES, i.e nodes that are connected by an edge, have the same color.
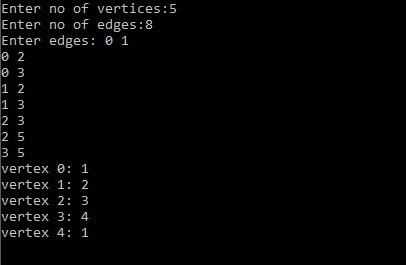
/***OUTPUT***/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 | #include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h> int g[10][10],color[10],n; int main() { void graph(int k); void display(); int e,i,j,v1,v2; //making an adjacency matrix printf("Enter no of vertices:"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("Enter no of edges:"); scanf("%d",&e); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { color[i] = 0; //setting colors of all vertices to 0 for(j=0;j<n;j++) { g[i][j] = 0; } } printf("Enter edges: "); for(i=1;i<=e;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&v1,&v2); g[v1][v2] = 1; g[v2][v1] = 1; } for(i=0;i<n;i++) graph(i); //passing each vertex one by one to the method "graph" display(); return 0; getch(); } void graph(int k) { int i; color[k] = 1;//setting the color of the vertex initially to 1 for(i=0;i<k;i++) { if(g[i][k]!=0 && color[i] == color[k]) /*here, we check each whether we have an edge between vertex" i " and the vertex we passed to the function. suppose we have an edge, further we see whether both vertices have a same color or not. if yes, then the color is incremented to 2, else it stays 1*/ { color[k] = color[k]+1; } } } void display() { int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("vertex %d: %d\n",i,color[i]); } } |
/***OUTPUT***/


Comments
Post a Comment